The typical situation where an email password is compromised is from a successful phishing attempt – password was leaked to a fake Microsoft or Google site after clicking on a suspicious email and authenticating with credentials.
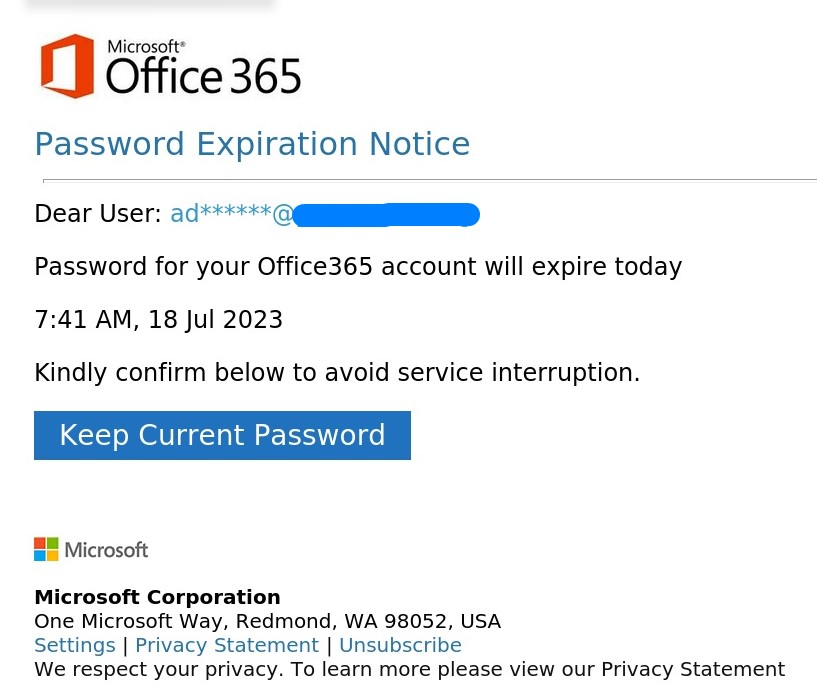
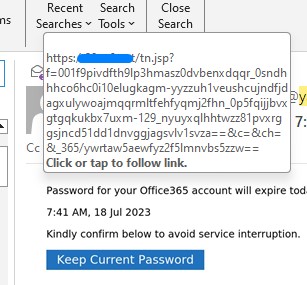
First picture shows a typical phishing email. Subsequent picture shows phisher's destination site when hovering mouse over the link.
The perpetrator will then authenticated and maintain a persistent session on web mail, stealthily monitor your email communications and then get information on the correspondence that you have.
This is particularly damaging if the email account is a business account. It does not matter if you are a trade creditor or trade debtor. Once these details are available to them, they can construct another email engineered to trick either you (posing as your supplier) or to your supplier (posing as you) and request a pending payment to be paid to another bank account due to some banking issues.
A misspelled domain (1 as l or vice versa) or a similar sounding domain will be registered and a fake email account created. It will be so similar to such an extend that other than the domain name, the sender’s name (even case sensitively similar), signature, message content and sentence construct will be exactly the same.
The victim will then be instructed to pay to the scammer’s bank account and may realize only when supplier start asking them for payment.
Some steps that IT administrators can take are:
- Enforce Multi-factor authentication for email access using mobile OTP or authenticator apps.
- Train users to identify phishing email through phishing simulator (Microsoft or third party) and conduct constant training for new and existing users.
- Enforce modern authentication, password strength, complexity and set a password expiry period.
- Force sign-out all sessions for each password change to prevent session using cached credential.
- For users not accessing email externally, disable Outlook Web Access (webmail), insecure protocol, POP3 and IMAP access.
- Monitor Azure AD sign-in logs for suspicious failed or successful sign-ins outside of your geographic location as it may indicate successful phish attempts. If necessary, force password reset and sign-out all sessions.
- Tag external emails with warning message and educate users on why an email is tagged as external when it seems to be from someone within the organization and to be cautious of attachments/links within such emails. Explain to users that emails tagged as external are sent from external parties even though it may appears to be from someone within the organization. All such emails especially the later should be handled with caution.